Development and commercialization of "ped UT-Heart", a cardiac simulator for supporting decisions of surgical procedures to save lives and improve the quality of life for children with congenital heart disease has been selected by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED), and clinical trials and service development will be carried out in the future.PIA Co., Ltd. (Headquarters: Shinagawa-ku, Tokyo, Representative Director: Kiyoshi Nakanishi, hereinafter referred to as “PIA”) and Japan Medical Device Corporation (Headquarters: Kawasaki City, Kanagawa Prefecture, Representative Directors: OKANO Takafumi, CHIBA Shuichi, hereinafter referred to as “JMD”) have been selected for the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (AMED) projects as PIA is the representative body and JMD is the co-organization.
The project name is “Development and commercialization of “ped UT-Heart”, a cardiac simulator for supporting decisions of surgical procedures to save lives and improve the quality of life for children with congenital heart disease.
We will advance the results of the “ped UT-Heart” research and development so far, conduct clinical trials within this project period, proceed with service verification and service design, and aim to apply for approval of medical devices.
■Background, needs
Congenital heart disease accounts for 1 in 100 newborns and is the most common cause of death in newborn infants.
The heart of the target child is small, the three-dimensional structure is extremely complex, and the variation of lesions is large, so surgical treatment is very difficult.
In addition, patients suffer from residual disease and sequelae even after surgery, and their quality of life (QOL) is not satisfactory.
Therefore, in the surgical treatment of congenital heart disease, it is necessary not only to save the patient’s life, but also to determine the treatment strategy on the premise of maintaining good QOL over the long term of the growing pediatric patient.
For this purpose, it is necessary to appropriately predict the hemodynamics including postoperative cardiac function before surgery and decide on a treatment plan.
However, there is not enough anatomical and physiological evidence for surgical decisions, and thus we rely on the experience and intuition of cardiac surgeons.
■Development of Heart Simulator and ped UT-Heart
The University of Tokyo and UT-Heart Research Inc. have developed UT-Heart, a world-first heart simulator that can faithfully reproduce a patient’s heart in silico based on molecular and cellular functions using a computer-based simulation model.
By using a patient’s heart model reproduced on a computer, it is possible to predict hemodynamics including postoperative cardiac function by trying various virtual surgeries before the actual surgery, and to realize tailor-made medical care that selects the most suitable surgical method for the patient.
Based on this “UT-Heart” system, we began the development of a new system “ped UT-Heart” specialized in the analysis of childhood congenital heart disease in 2020, and have conducted multicenter clinical trials to evaluate its usefulness.
■Features of ped UT-Heart
ped UT-Heart is a simulator that can quantitatively predict postoperative cardiac function and hemodynamics of multiple surgical procedures based on the patient’s preoperative clinical information for congenital heart disease in children with extremely complex structures and hemodynamics.
This is a system in which cardiac surgeons do not decide surgical procedures and treatment plans based solely on their own experience and subjectivity, but objectively analyze the patient’s clinical information with a high-performance computer and propose appropriate surgical procedures based on the results, thereby supporting appropriate surgical procedures.
It supports cardiac surgery for pediatric congenital heart disease, which requires advanced technology and outstanding clinical experience, by providing objective judgment materials that are mathematically calculated based on the patient’s clinical data, and predicts the postoperative state of multiple possible surgeries before surgery. Therefore surgeons can select the best one from among them, improving the survival rate of patients with congenital heart disease, and improving long-term prognosis which leads to improved quality of life throughout life.
■Effects of UT-Heart
The use of this device increases the likelihood that surgeons can choose the most suitable surgical procedure for their patients, thereby improving the patient’s lifelong quality of life by not only increasing the life-saving rate of technically challenging congenital heart disease surgeries, but also reducing postoperative residual disease and sequelae.
■This project
This project was selected for AMED’s Advanced Medical Devices and Systems Technology Development Project (Fundamental Technology Development Project) from July 2020 to March 2023, and has been selected again by AMED for the second time in a row. The new grant period is from April 2023 to March 2026. Based on the results of the efficacy verification in clinical trials so far, we will aim for medical device approval by conducting clinical trials, building a service provision system in parallel, designing it as a cloud service and preparing the QMS of the service.
■ Appearance of the service
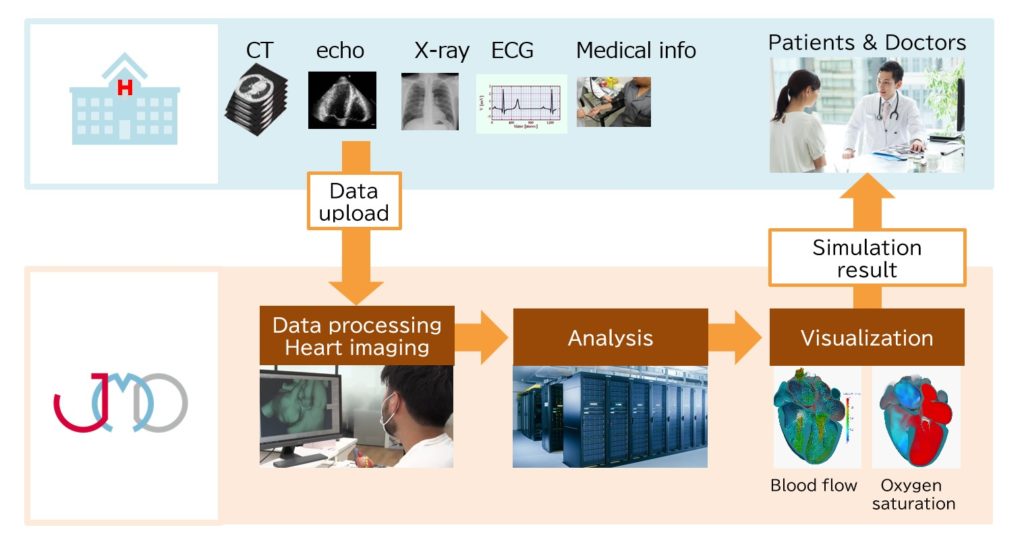
The UT-Heart clinical decision support service will be provided as a cloud-based service.
As a result, medical institutions can obtain simulation results simply by providing conventional medical data without introducing equipment or assigning specialized engineers. JMD performs necessary image processing based on data uploaded from medical institutions, analyzes it with the heart simulator, creates a report from a medical perspective based on the analysis results, and provides the results to doctors.
■Vision of society
If this simulator is widely used around the world, it will be possible for patients with complex congenital heart disease, which is extremely difficult to treat surgically, to receive the best surgical intervention, predicted using mathematical calculations based on each person’s preoperative heart morphology and hemodynamics.
As a result, it is expected to contribute to the reduction of medical costs in society as a whole, as well as improving the life-saving rate of surgery, maintaining good QOL throughout life after surgery, avoiding conditions requiring treatment or the risk of reoperation, and sudden death.
■Project Overview
R&D Project Title
Development and commercialization of “ped UT-Heart”, a cardiac simulator for supporting decisions of surgical procedures to save lives and improve the quality of life for children with congenital heart disease.
Publicly offered (project name)
Medical-Engineering Collaboration Innovation Promotion Project Development and Commercialization project
R&D period:
April 1, 2023 to March 31, 2026 (3 years)
R&D Representative
SHIRAISHI Isao MD, Ph.D. (PIA Co., Ltd)
Representative organization:
PIA Co., Ltd
Collaborative Organizations
Japan Medical Device Corporation
National Cerebral and Cardiovascular Center,
Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, The University of Tokyo,
UT-Heart Inc.
Cross Medical, Inc.
■About Japan Medical Device Corporation (JMD)
JMD is a company that researches, develops and provides a new medical device computer simulation service that utilizes the heart simulator (UT-Heart) created by the University of Tokyo over a period of more than 20 years.
The heart simulator is the world’s highest technology that can faithfully reproduce the movement of an individual’s heart in detail by using clinical data including CT and ultrasound images as input data and calculating electrical and mechanical behavior at the molecular level by utilizing the computing power of a supercomputer.
Precise simulations in the medical field require cutting-edge skills and know-how to express medical knowledge in an engineering manner (medical-engineering collaboration) and to calculate at the highest speed using the latest computers (computer science). JMD has these abilities and is developing in collaboration with Japan’s top research institutes and demonstration institutions to build and provide a one-stop cloud service that includes medical data processing and simulation result imaging (pre-post processing) prior to computation.
By combining heart simulator technology, AI and other technologies, we aim to improve the quality of medical care through the verification and prediction of heart diseases and the provision of other medical and health screening services.
Home Page https://jmd-corp.com
